By Yaseen Jangikhan
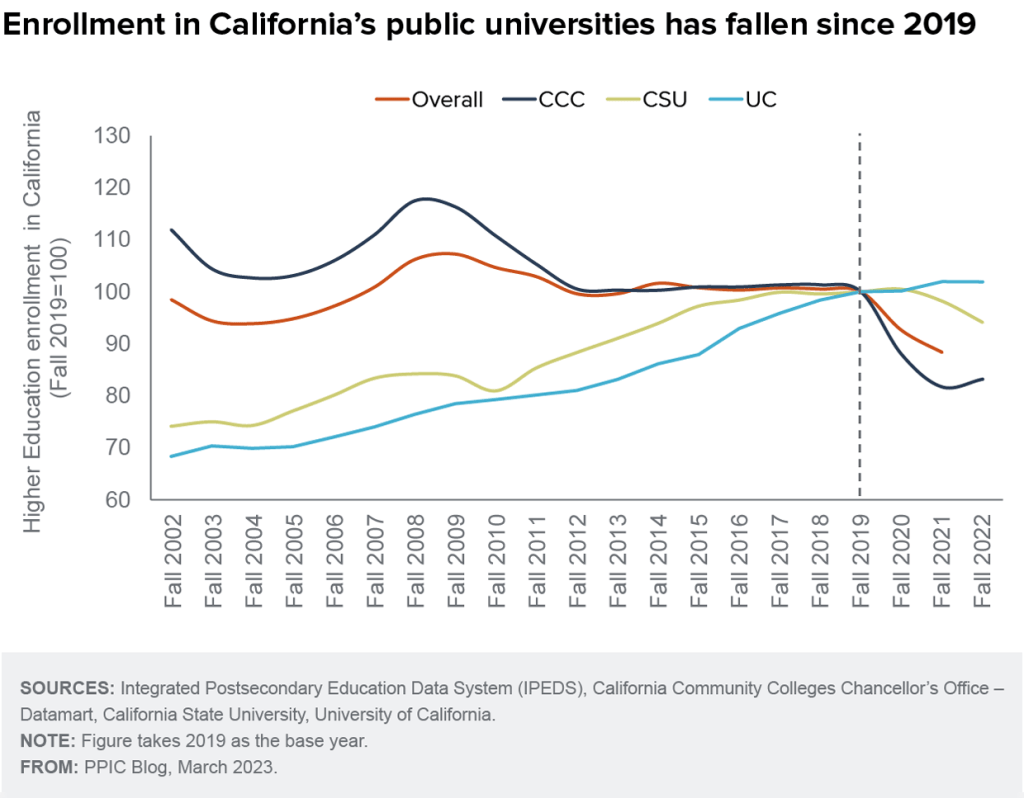
A recent analysis highlighted a troubling trend inside the California State University CSU system: a considerable drop in enrollment over the last four years. According to the analysis, which examined enrollment statistics from 2019 to 2023, there was a 6% reduction in student enrollment across all CSU campuses.
This enrollment reduction, while concerning, is partially unexpected given the numerous challenges and upheavals that higher education institutions have faced in recent years. Factors such as the COVID-19 pandemic, economic uncertainty, demographic changes, and adjustments in student choices are all possible contributors to this declining trend.
The COVID-19 epidemic has had a significant influence on higher education institutions globally. The abrupt transition to distant learning, health concerns, and financial challenges have resulted in major changes in student behavior and enrollment patterns. Due to the uncertainty caused by the pandemic, many students may have chosen to postpone their studies or seek different courses.
Furthermore, changes in student tastes and priorities could have contributed to decreased CSU enrollment. Enrollment stakeholders, including legislators, educators, and community leaders, must collaborate to ensure the sustained success and accessibility of higher education in California.
Despite efforts to ensure affordability, the cost of attending college continues to grow. Tuition fees, living expenditures, and other related charges can create significant financial barriers for students and their families, influencing enrollment decisions. Higher education is becoming more competitive, with alternative educational paths gaining popularity. Students may choose vocational training, online education, or career development programs over regular four-year university programs offered by the CSU system.
Changes in government regulations, administrative actions, or academic requirements within the CSU system may have an impact on enrollment trends. Admissions standards, financial aid availability, and program offers all have the potential to impact students’ enrollment decisions. A decline in enrollment can have a considerable financial impact on the CSU system, altering income streams and budget allocation. To ensure long-term viability, institutions may need to reconsider their financial strategy, reduce operations, and explore new funding sources. Lower enrollment numbers may demand a review of academic programs and course offerings across the CSU system.
To address changing student demands, institutions may need to emphasize high-demand programs, consolidate resources, or experiment with new ways.
Providing fair access to higher education is a top focus for the CSU system. To address enrollment decreases, outreach campaigns, financial assistance programs, and support services should be implemented to enhance access and retention for underrepresented and underserved student populations. Enrollment trends give useful information for long-term planning in the CSU system.
Institutions must anticipate future issues, adjust methods, and innovate to be robust in today’s dynamic higher education context. From 2019 to 2023, enrollment in the California State University system fell by 6%, highlighting the various issues that higher education institutions face. Understanding the factors contributing to this reduction and applying preventative actions will enable the CSU system to solve the issue while remaining true to its objective of offering accessible, affordable, and high-quality education.